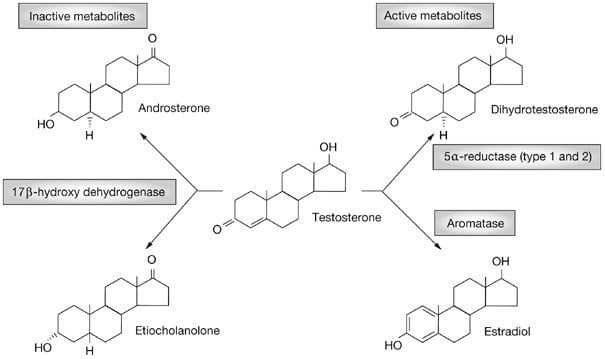
Etiocholanolone a Testosterone metabolite is likely to blame.
testosterone overdose in animals needs treatment with naloxone to reverse etiocholanolne testosterone flu
Etiocholanolone (3a-hydroxy-5p-androstan-17-one) is a naturally occurring steroid metabolite arising from androgens of gonadal and adrenocortical origin. It has no known hormonal activity but will regularly produce fever only in man when administered intra- muscularly in its free unconjugated form. characterisitically am I’m injecting of etiocholanolone produces a locks inflammatory redaction which is followed 6-8 hours by fever being a nonantigenic human pyrogen it has been used in studies of the pathogenesis of fever and sterile inflammation For this reason it also provides an interesting model for the study of acute phase reactants.
Progesterone can also convert to etiocholanolone anabolics like trenbolone causing flu
Study
The conversion of intravenously administered 4-14C progesterone to urinary C19 steroids was studied in 4 selected women and one normal man. Androsterone was isolated from the glucuronide fraction in 3 of the women and in the male subject, and from the sulfate fraction in one of the women and in the male. Etiocholanolone was isolated from the glucuronide fraction only in the male. The conversion of progesterone to androsterone was about 0.02% in the women, and there was no apparent correlation with their endogenous C19 steroid milieu. In the male subject, there was 0.3% conversion to androsterone and about 0.1% conversion to etiocholanolone. These values are much lower than the conversion observed in certain nonhuman primates and in one reported study of a pregnant woman.
Last edited:
